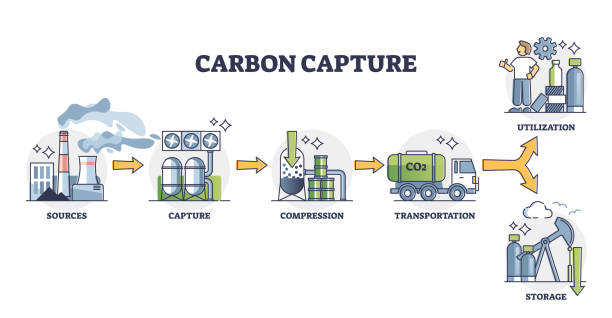
Carbon capture refers to the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes, such as power generation, before they are released into the atmosphere. This technology is seen as a key tool in mitigating the effects of climate change, as it can help to reduce the amount of CO2 emissions produced by industry and other sources.
There are several different technologies for carbon capture, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most promising technologies include:
Post-combustion capture: Post-combustion capture technology is used to capture CO2 emissions from power plants and other industrial processes that burn fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil. The technology works by capturing the CO2 emissions from the flue gases produced by the combustion process and storing them for later use or disposal.
Pre-combustion capture: Pre-combustion capture technology is used to capture CO2 emissions from power plants and other industrial processes that use gasification or reforming to produce synthesis gas, which is then burned to produce electricity. The technology works by capturing the CO2 emissions produced during the gasification or reforming process and storing them for later use or disposal.
Oxy-fuel combustion: Oxy-fuel combustion is a technology that uses pure oxygen, instead of air, in the combustion process to produce a flue gas that is rich in CO2. This makes it easier to capture and store the CO2 emissions produced by the process.
Chemical looping: Chemical looping is a technology that uses metal oxides, such as iron oxide, as a medium to transfer oxygen from air to a fuel, such as coal or natural gas. This produces a flue gas that is rich in CO2, which can then be easily captured and stored.
Direct air capture: Direct air capture is a technology that uses large machines to capture CO2 directly from the atmosphere. The machines work by absorbing CO2 from the air and then releasing it into a storage facility for later use or disposal.
Each of these technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them will depend on a number of factors, including the specific application, the availability of resources and infrastructure, and the cost and efficiency of the technology.
For example, post-combustion capture is a well-established technology that has been used for many years in various industrial processes, and it is relatively easy to retrofit existing power plants to use this technology. However, it is also relatively expensive, as it requires a significant amount of energy to capture and store the CO2 emissions.
Pre-combustion capture, on the other hand, is a newer technology that is still being developed and is not yet widely used. However, it has the advantage of being more efficient than post-combustion capture, as it captures the CO2 emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Oxy-fuel combustion is a promising technology that has the advantage of producing a flue gas that is rich in CO2, making it easier to capture and store the emissions. However, it is also relatively expensive, as it requires a significant amount of energy to produce the pure oxygen needed for the combustion process.
Chemical looping is a newer technology that is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be highly efficient and cost-effective. However, it is also relatively untested, and more research is needed to determine its feasibility and commercial viability.
Direct air capture is a promising technology that has the advantage of capturing CO2 directly from the atmosphere, regardless of its source. However, it is also relatively expensive, and it requires a significant amount of energy to operate the machines and transport the captured CO2 to a storage facility.
In conclusion, there are several different technologies for carbon capture, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice between them will depend on a number of factors, including the specific application, the availability of resources and infrastructure, and the cost and efficiency of the technology. However, regardless of the technology used, carbon capture is seen as an important tool in mitigating the effects of climate change, as it can help to reduce the amount of CO2 emissions produced by industry and other sources. As such, it is an area of ongoing research and development, and it is likely that new and improved technologies will emerge in the coming years.